
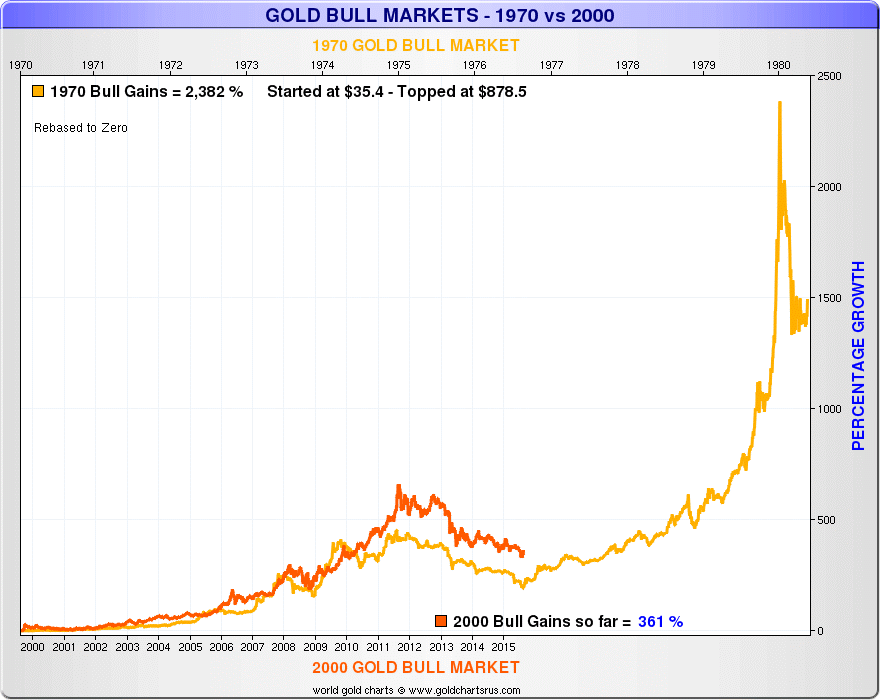
Section 13 authorized reserve banks to accept as collateral for discount loans assets that financed agricultural, commercial, and industrial activity but prohibited them from accepting as collateral “notes, drafts, or bills covering merely investments or issued or drawn for the purpose of carrying or trading in stocks, bonds or other investment securities, except bonds and notes of the Government of the United States” (Federal Reserve Act 1913). The Board’s opinion stemmed from the text of the act. The Board asserted that the “Federal Reserve Act does not … contemplate the use of the resources of the Federal Reserve Banks for the creation or extension of speculative credit” (Chandler 1971, 56). The governors of many Federal Reserve Banks and a majority of the Federal Reserve Board believed stock-market speculation diverted resources from productive uses, like commerce and industry. Borrowed money poured into equity markets, and stock prices soared. The stocks that they bought served as collateral for the loan. Purchasers put down a fraction of the price, typically 10 percent, and borrowed the rest. A new industry of brokerage houses, investment trusts, and margin accounts enabled ordinary people to purchase corporate equities with borrowed funds. Ordinary men and women invested growing sums in stocks and bonds. Automobiles, telephones, and other new technologies proliferated. The financial boom occurred during an era of optimism. (Source: FRED, (graph by: Sam Marshall, Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond) Enlarge The index did not reach the 1929 high again until November 23, 1954.

The index declined until July 8, 1932, when it closed at $41.22.
As shown in the figure, the index peaked on September 3, 1929, closing at 381.17. Minor tick marks indicate the first trading day of the year. Chart 1: Dow Jones Industrial Average Index daily closing price, January 2, 1920, to December 31, 1954. The Dow did not return to its pre-crash heights until November 1954. The slide continued through the summer of 1932, when the Dow closed at 41.22, its lowest value of the twentieth century, 89 percent below its peak. By mid-November, the Dow had lost almost half of its value. On the following day, Black Tuesday, the market dropped nearly 12 percent. On Black Monday, October 28, 1929, the Dow declined nearly 13 percent.
The epic boom ended in a cataclysmic bust. After prices peaked, economist Irving Fisher proclaimed, “stock prices have reached ‘what looks like a permanently high plateau.’” 1 The Dow Jones Industrial Average increased six-fold from sixty-three in August 1921 to 381 in September 1929. Share prices rose to unprecedented heights. The Roaring Twenties roared loudest and longest on the New York Stock Exchange.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
